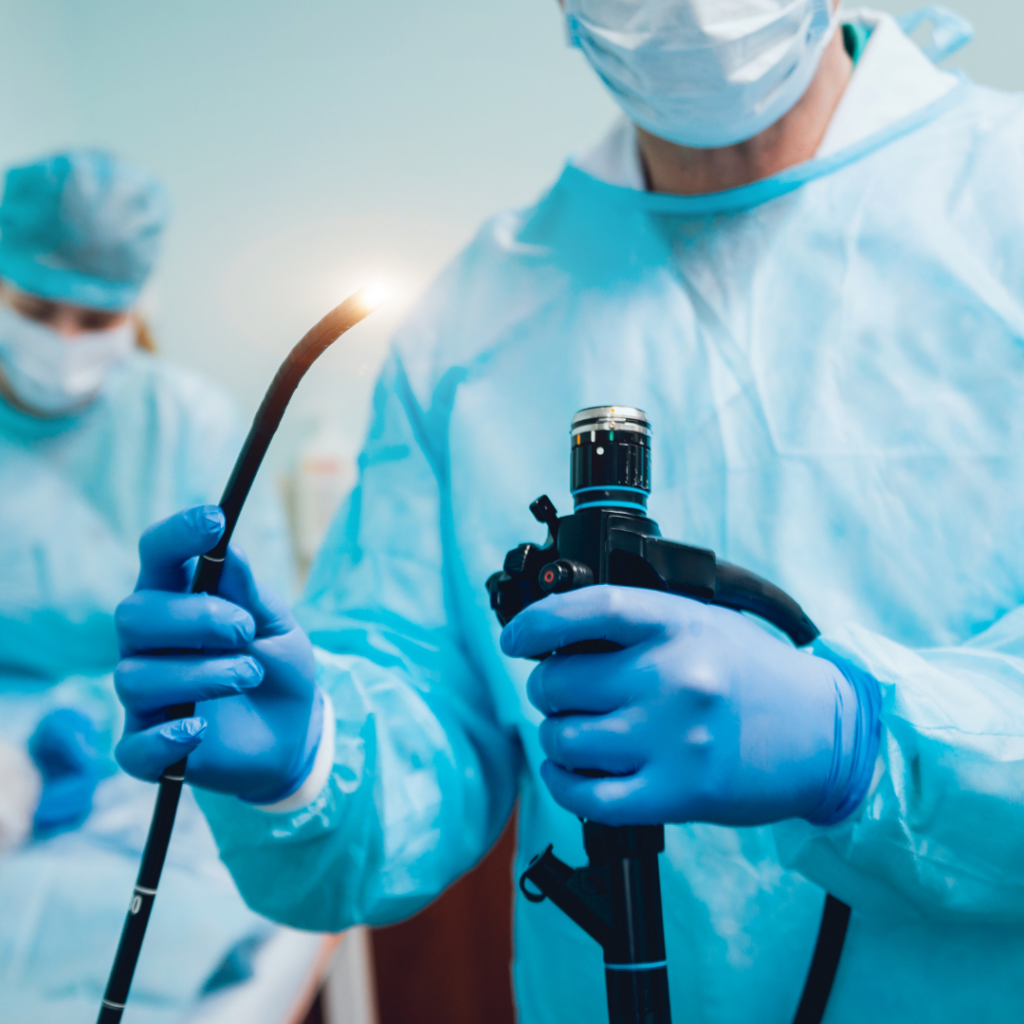
What is a gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy is a medical procedure in which an endoscope is inserted through the mouth into the stomach. In this way, it is possible to examine the mucosa of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. During the examination, a test sample can be taken and treatment procedures can be performed. Gastroscopy is a very effective method for diagnosing and treating diseases of the upper sedet tract.
Why is gastroscopy necessary?
Gastroscopies are often used to diagnose the causes of gastrointestinal symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), heartburn, abdominal pain, indigestion, and vomiting. It is also used to find out the causes of anemia and unexplained weight loss.
In addition, gastroscopies can be used to treat various diseases. For example, to expand the esophagus, to stop bleeding, or to remove a stomach polyp.
How to prepare for gastroscopy?
Before gastroscopies, it is important that the patient should not eat for at least 6 hours and drink for 2 hours. The doctor may recommend temporarily stopping the administration of certain medications, such as blood thinners, before gastroscopies.
Procedure
During a gastroscopy, the endoscope is guided through the mouth into the esophagus, the palate and the duodenum. This area can be sprayed with local anesthetic gum to reduce the gag reflex and facilitate gastroscope advancement. Amsel Clinicus packages the procedure with narcosis, so you don’t feel uncomfortable.
Recovery
Discomfort, gas and abdominal and throat pain may occur after gastroscopy. It’s normal according to the examination, Ning møstøb within a few hours. The cucumber can also be cast the next day.
Apart from gastroscopies, there are no significant restrictions on starting to eat. Patients can enter Minna 30–60 minutes after the procedure. I’m not allowed to drive the car the next morning, because the tranquilizer administered reduces the reaction speed.
Risk
Although gastroscopies are generally considered to be a safe procedure, complications such as allergic reactions, aspiration pneumonia, bleeding or perforation (intestinal tract wall mulgustus) may occur. Tüsistuses occur rarely, however, and are mainly related to either polypectomy or other treatment procedures.
The results
The primary results of the procedure are discussed with the patient before being sent to the hospital. If you have a test sample, you can get results for a day or a few weeks later, depending on the necessary analyses.
Why do gastroscopy under anesthesia?
The study is informative, but it can be unpleasant for the patient when it is done while lying down. Anesthesia allows the procedure to be as comfortable as possible for the patient, while maintaining the opportunity to get accurate and clear information about the state of the digestive tract.
Amsel Clinic offers the opportunity to perform a gastroscopy in general anesthesia Teile sobival ajal, valutult Ning muretult.